请注意,本文编写于 614 天前,最后修改于 614 天前,其中某些信息可能已经过时。
目录
传统IO过程
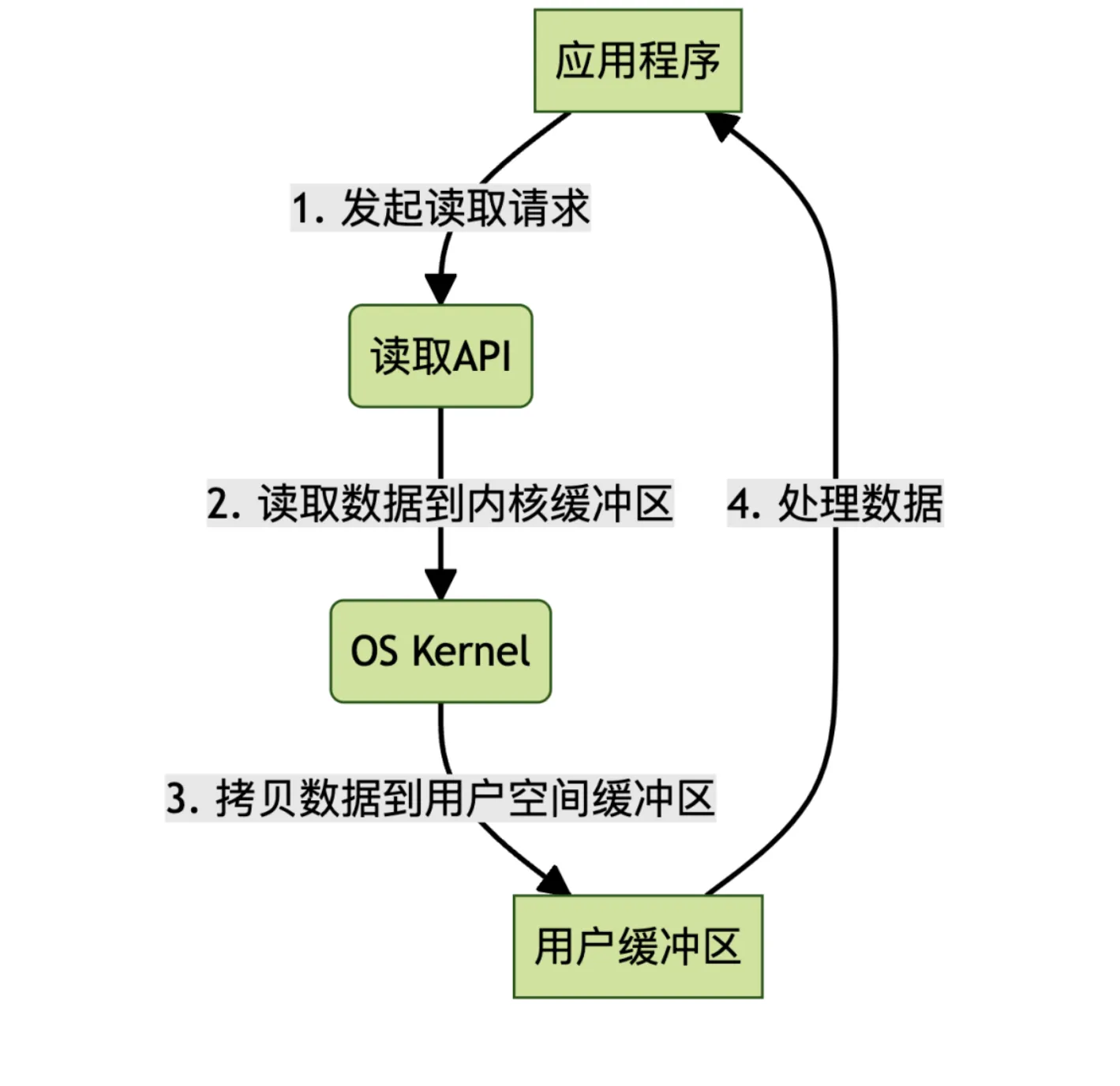
- 应用程序先发起读操作,准备读取数据了;
- 内核将数据从硬盘或外部存储读取到内核缓冲区;
- 内核将数据从内核缓冲区拷贝到用户缓冲区;
- 应用程序读取用户缓冲区的数据进行处理加工;
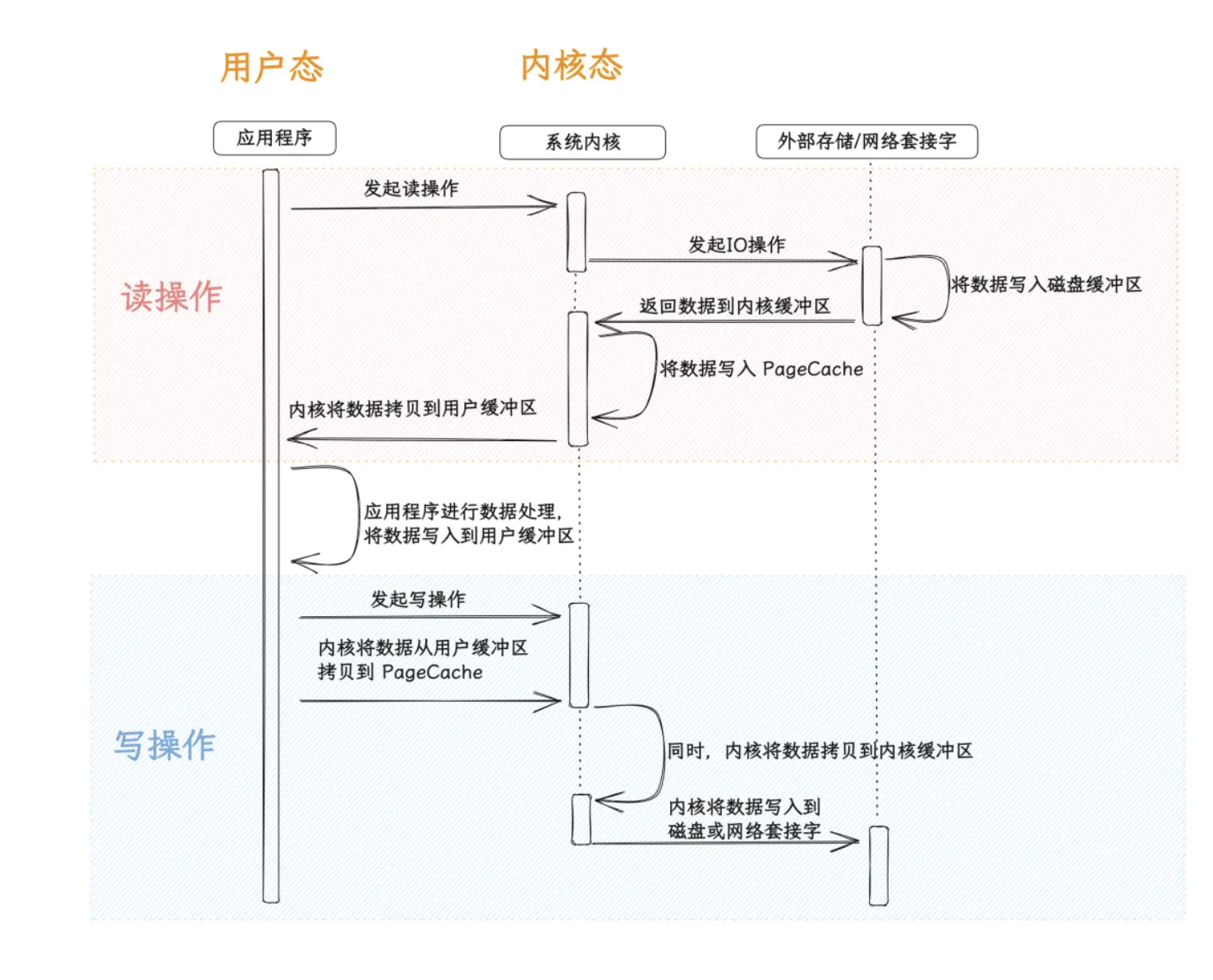
磁盘缓冲区
磁盘缓冲区是计算机内存中用于暂存从磁盘读取的数据或将数据写入磁盘之前的临时存储区域。它是一种优化磁盘 I/O 操作的机制,通过利用内存的快速访问速度,减少对慢速磁盘的频繁访问,提高数据读取和写入的性能和效率。
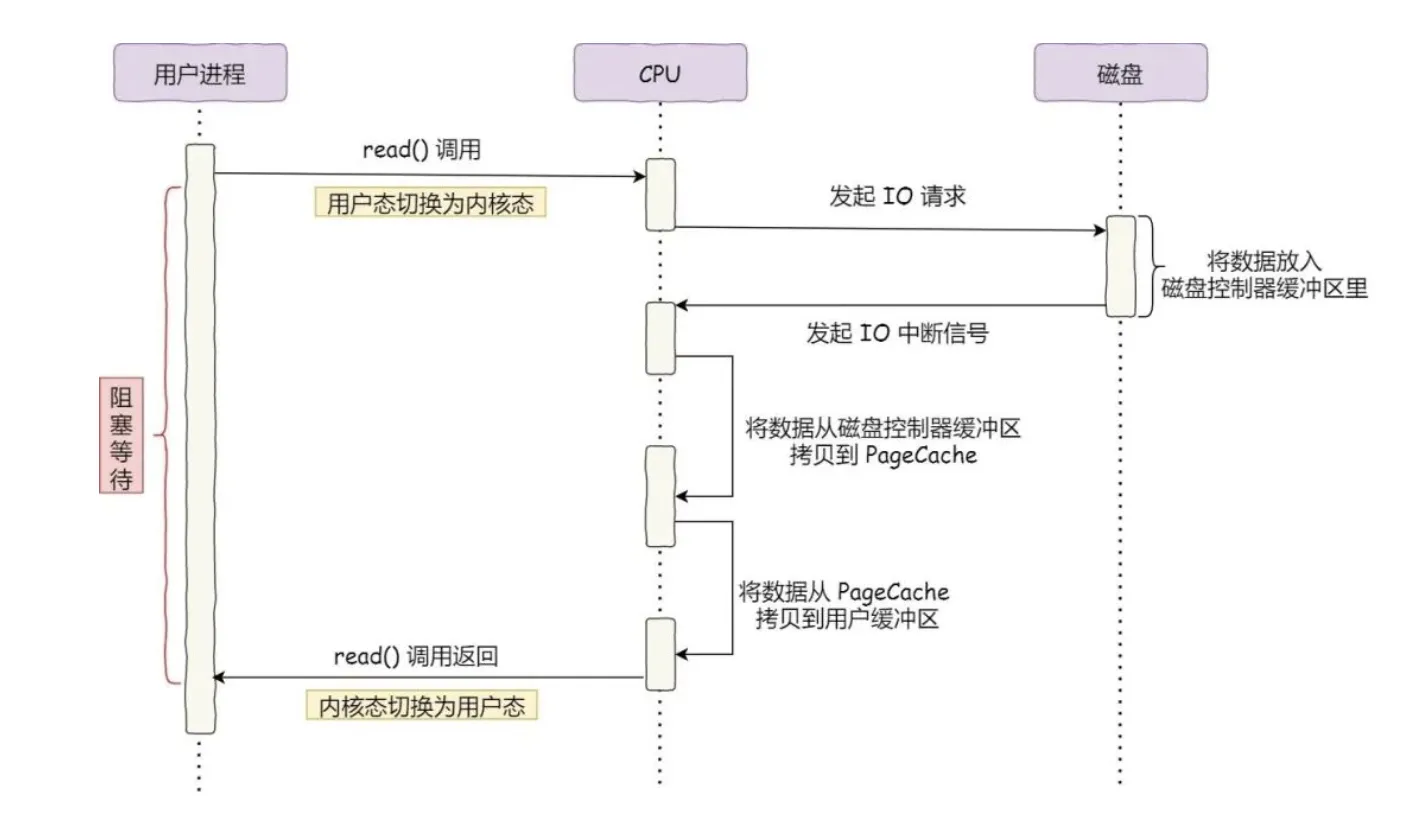
读
- 首先应用程序向内核发起读请求,这时候进行一次模式切换了,从用户态切换到内核态;
- 内核向外部存储或网络套接字发起读操作;
- 将数据写入磁盘缓冲区;
- 系统内核将数据从磁盘缓冲区拷贝到内核缓冲区,顺便再将一份(或者一部分)拷贝到 PageCache;
- 内核将数据拷贝到用户缓冲区,供应用程序处理。此时又进行一次模态切换,从内核态切换回用户态;
写
应用程序向内核发起写请求,这时候进行一次模式切换了,从用户态切换到内核态; 内核将要写入的数据从用户缓冲区拷贝到 PageCache,同时将数据拷贝到内核缓冲区; 然后内核将数据写入到磁盘缓冲区,从而写入磁盘,或者直接写入网络套接字。
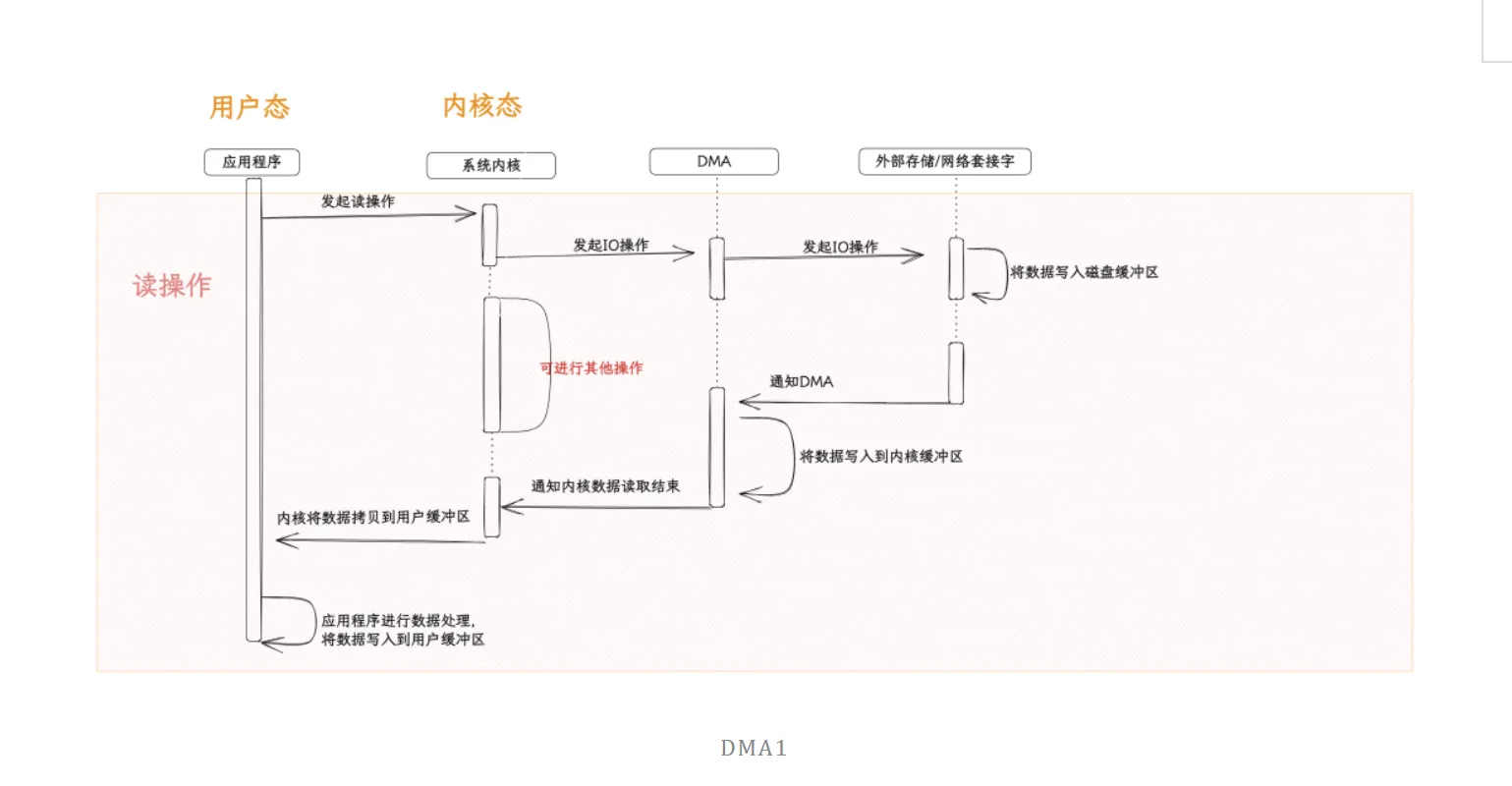
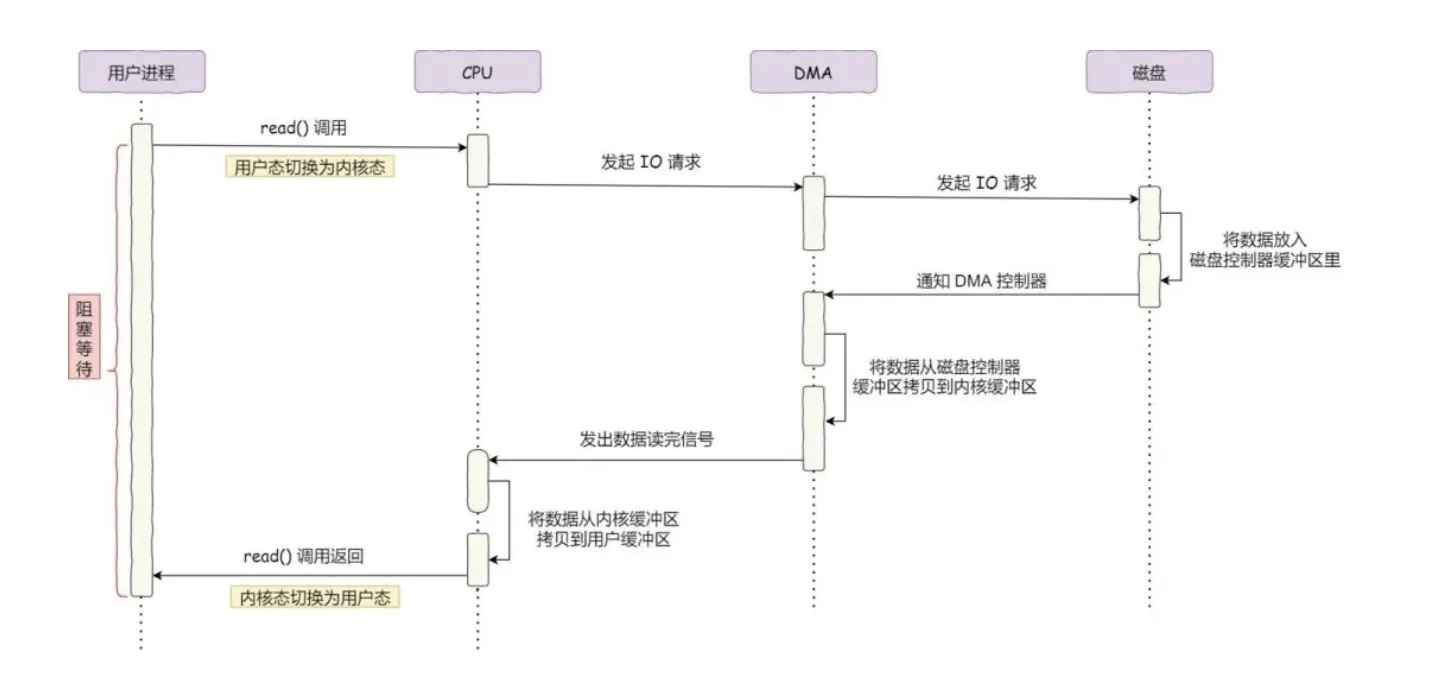
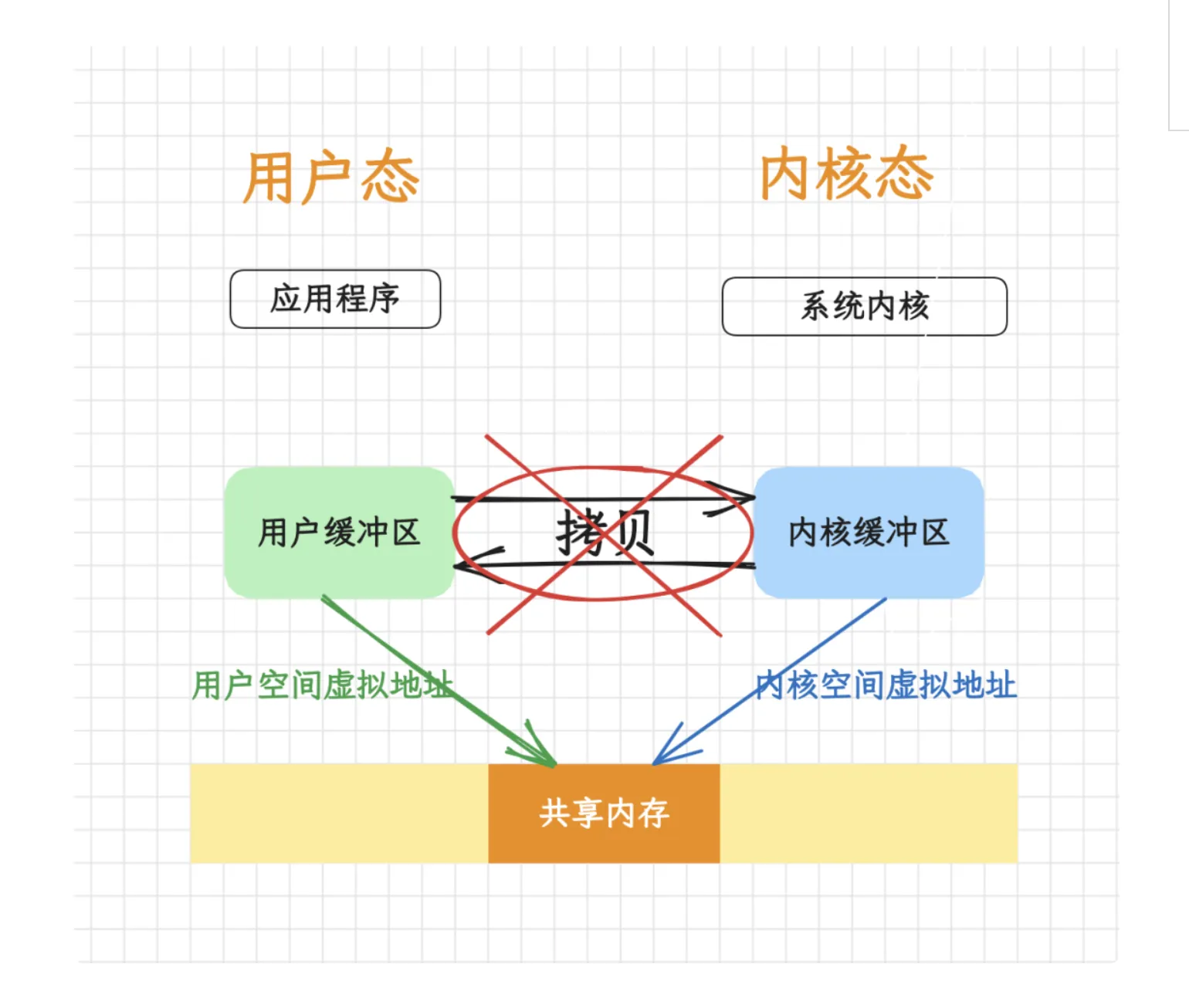
DMA直接内存访问
共享内存
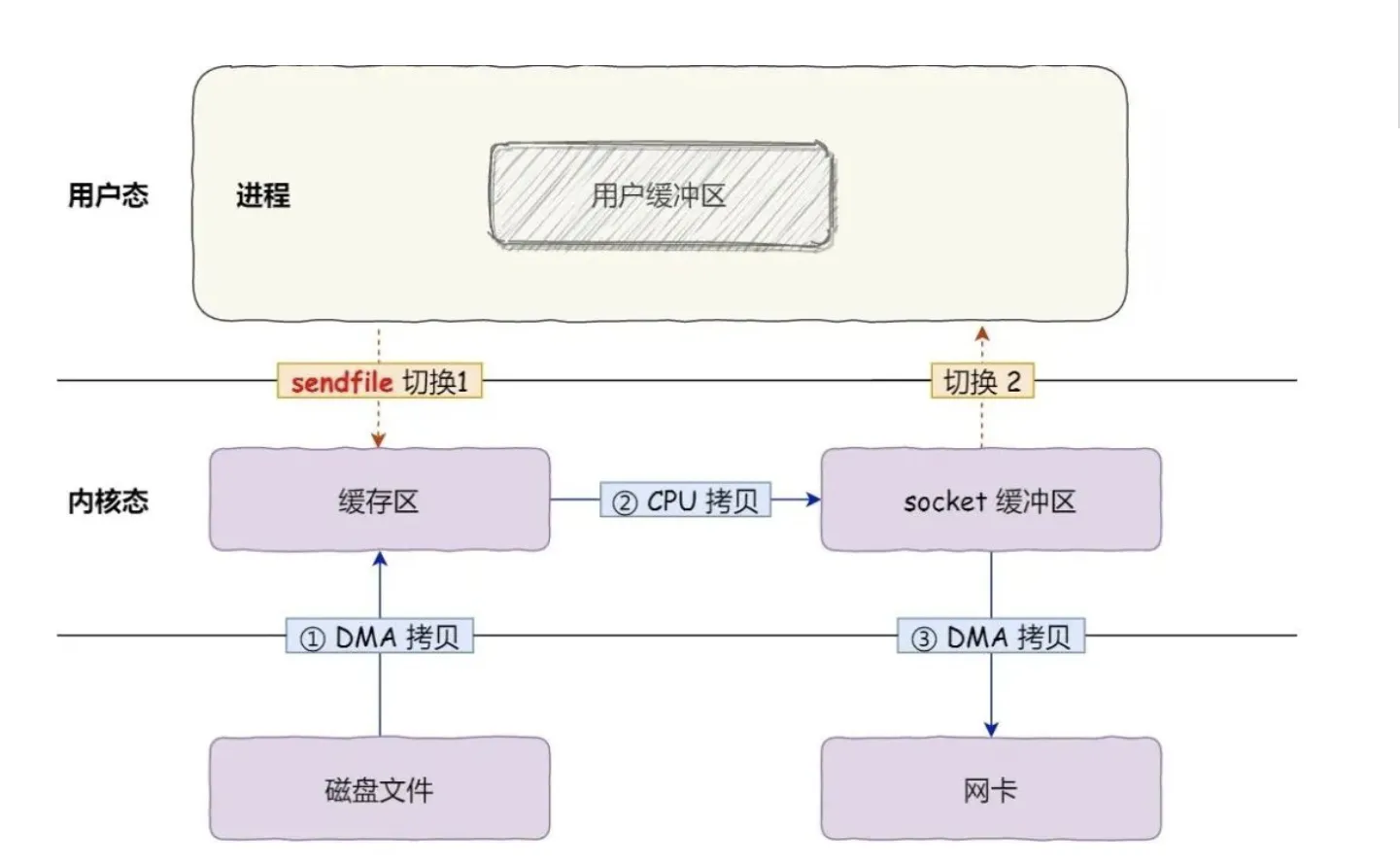
sendfile
它的前两个参数分别是目的端和源端的文件描述符,后面两个参数是源端的偏移量和复制数据的长度,返回值是实际复制数据的长度。
首先,它可以替代前面的 read() 和 write() 这两个系统调用,这样就可以减少一次系统调用,也就减少了 2 次上下文切换的开销。
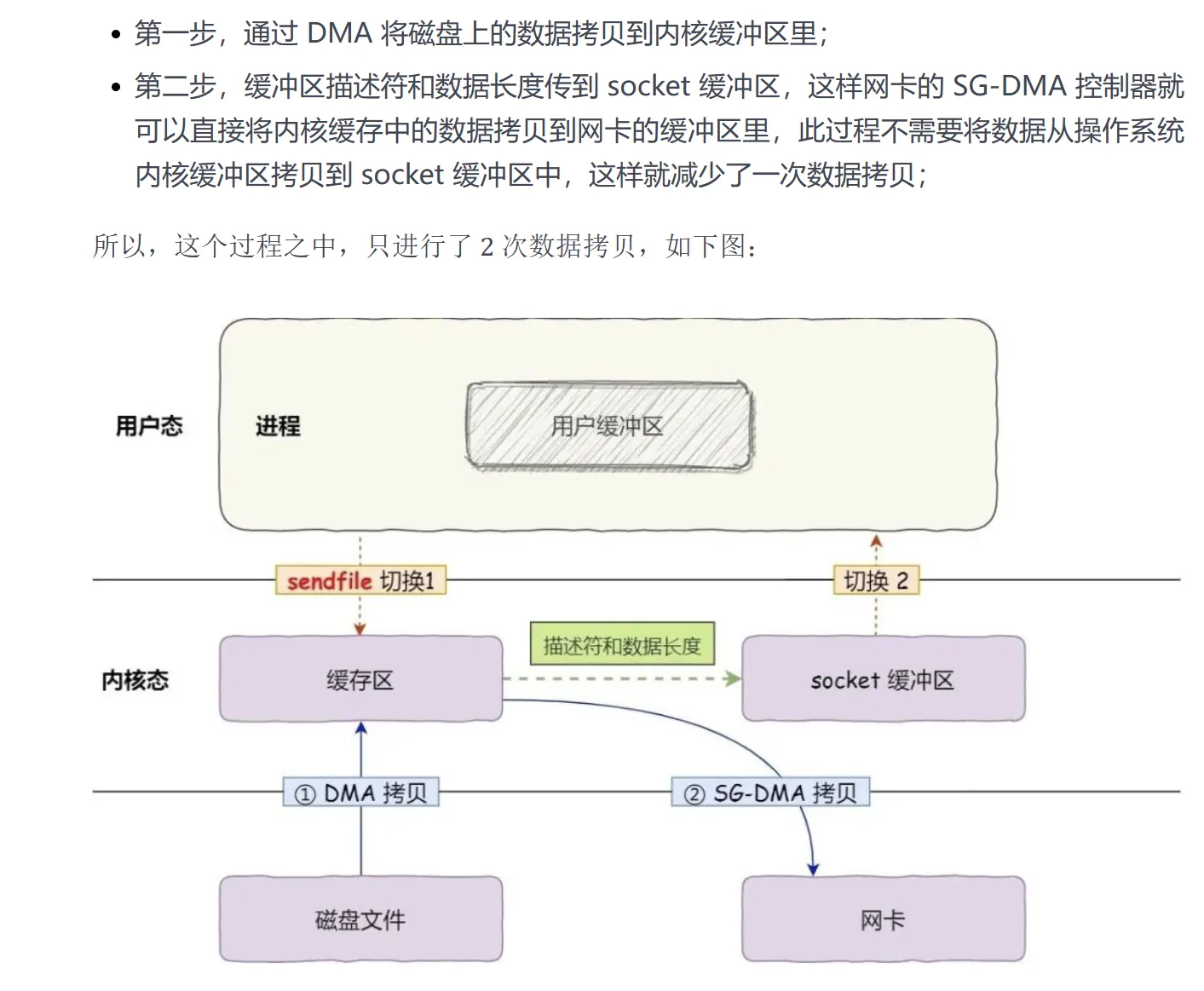
带有 scatter/gather 的 sendfile 方式
c#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <sys/sendfile.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int main() {
int source_fd = open("source_file.txt", O_RDONLY);
if (source_fd == -1) {
perror("Failed to open source file");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
int destination_fd = open("destination_file.txt", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_TRUNC, 0644);
if (destination_fd == -1) {
perror("Failed to open destination file");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
struct stat source_stat;
if (fstat(source_fd, &source_stat) == -1) {
perror("Failed to get source file information");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
off_t offset = 0;
ssize_t bytes_sent = sendfile(destination_fd, source_fd, &offset, source_stat.st_size);
if (bytes_sent == -1) {
perror("Failed to send file");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
printf("Successfully sent %zd bytes\n", bytes_sent);
close(source_fd);
close(destination_fd);
return 0;
}
本文作者:yowayimono
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!
目录