请注意,本文编写于 510 天前,最后修改于 506 天前,其中某些信息可能已经过时。
这段时间都在学习日语,准备考级,准备复习一下Java相关的知识,看一下源码什么的,现在就开始吧
ArrayList看似原理很简单,就是个可变长数组而已,但是还有不少可以学习的地方
首先看一下继承的接口
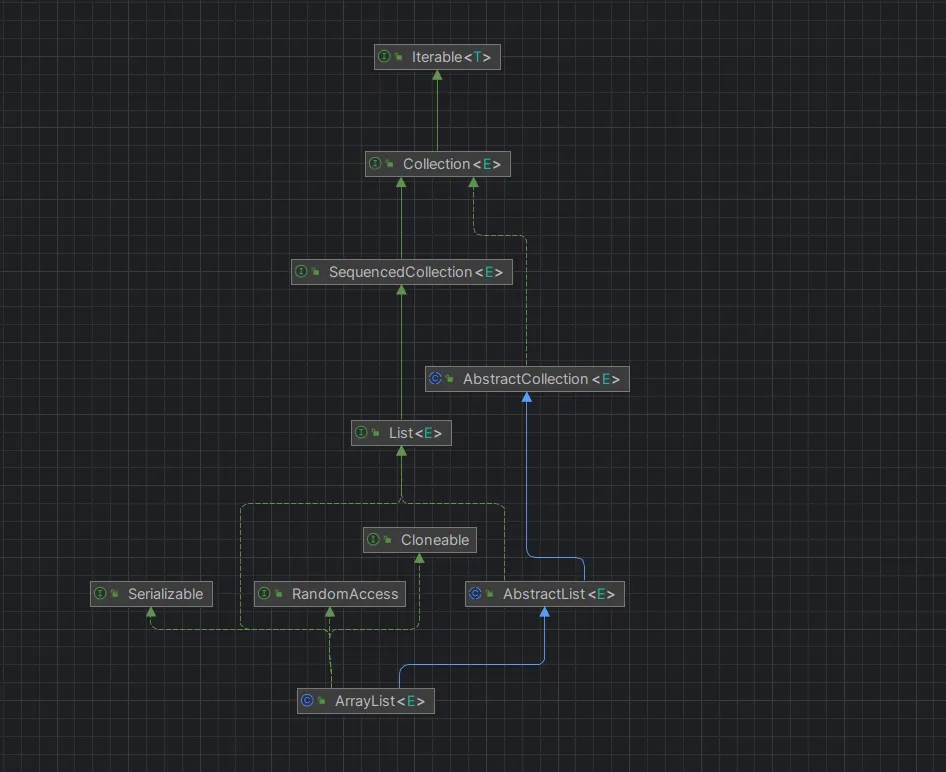
可以看到ArrayList实现了 List, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable等接口,后三个都是标记接口,分别标记随机访问,可以克隆,可序列化,所谓标记接口就是代表这个是可以做某种操作的空接口,Maker Interface,这些接口没有方法,都是空接口,一般对应的函数都会用instanceof去检查类是否被标记,或者直接自己实现对应方法,常见的Marker Interface还有,Remote,EventListener,Spring的Aware接口等
先看一下类定义
javapublic class ArrayList<E> extends AbstractList<E>
implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
接下来将一下基础函数,首先是属性
java @java.io.Serial
private static final long serialVersionUID = 8683452581122892189L; // 序列化版本
/**
* Default initial capacity.
*/
private static final int DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; // 默认大小
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for empty instances.
*/
private static final Object[] EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 传入容量为0
/**
* Shared empty array instance used for default sized empty instances. We
* distinguish this from EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA to know how much to inflate when
* first element is added.
*/
private static final Object[] DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA = {}; // 默认构造函数
/**
* The array buffer into which the elements of the ArrayList are stored.
* The capacity of the ArrayList is the length of this array buffer. Any
* empty ArrayList with elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
* will be expanded to DEFAULT_CAPACITY when the first element is added.
*/
transient Object[] elementData; // non-private to simplify nested class access 实际存储对象的数组
/**
* The size of the ArrayList (the number of elements it contains).
*
* @serial
*/
private int size; // 元素数量
在看一下构造函数
java public ArrayList(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity > 0) {
this.elementData = new Object[initialCapacity];
} else if (initialCapacity == 0) {
this.elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Illegal Capacity: "+
initialCapacity);
}
}
/**
* Constructs an empty list with an initial capacity of ten.
*/
public ArrayList() { // 延后扩容
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
/**
* Constructs a list containing the elements of the specified
* collection, in the order they are returned by the collection's
* iterator.
*
* @param c the collection whose elements are to be placed into this list
* @throws NullPointerException if the specified collection is null
*/
public ArrayList(Collection<? extends E> c) {
Object[] a = c.toArray();
if ((size = a.length) != 0) {
if (c.getClass() == ArrayList.class) {
elementData = a;
} else {
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(a, size, Object[].class);
}
} else {
// replace with empty array.
elementData = EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
}
接下来是add方法还有扩容逻辑
java
public void ensureCapacity(int minCapacity) {
if (minCapacity > elementData.length
&& !(elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA
&& minCapacity <= DEFAULT_CAPACITY)) {
modCount++;
grow(minCapacity);
}
}
private Object[] grow(int minCapacity) {
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
if (oldCapacity > 0 || elementData != DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
int newCapacity = ArraysSupport.newLength(oldCapacity,
minCapacity - oldCapacity, /* minimum growth */
oldCapacity >> 1 /* preferred growth */);
return elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
} else {
return elementData = new Object[Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity)];
}
}
private Object[] grow() {
return grow(size + 1);
}
/**
* This helper method split out from add(E) to keep method
* bytecode size under 35 (the -XX:MaxInlineSize default value),
* which helps when add(E) is called in a C1-compiled loop.
*/
private void add(E e, Object[] elementData, int s) {
if (s == elementData.length)
elementData = grow();
elementData[s] = e;
size = s + 1;
}
/**
* Appends the specified element to the end of this list.
*
* @param e element to be appended to this list
* @return {@code true} (as specified by {@link Collection#add})
*/
public boolean add(E e) {
modCount++;
add(e, elementData, size);
return true;
}
/**
* Inserts the specified element at the specified position in this
* list. Shifts the element currently at that position (if any) and
* any subsequent elements to the right (adds one to their indices).
*
* @param index index at which the specified element is to be inserted
* @param element element to be inserted
* @throws IndexOutOfBoundsException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public void add(int index, E element) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
modCount++;
final int s;
Object[] elementData;
if ((s = size) == (elementData = this.elementData).length)
elementData = grow();
System.arraycopy(elementData, index,
elementData, index + 1,
s - index);
elementData[index] = element;
size = s + 1;
}
其中modCount是操作次数,可以看到第一次扩容会判断是否是默认构造,是的话就初始化最小容量为10,这也就是为啥要搞两个共享空数组。modCount主要适用于快速失败机制,防止迭代器失效或者是并法修改导致的错误,默认的扩容机制是1.5倍扩容,这是选了省内存?
本文作者:yowayimono
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!