目录
启动过程
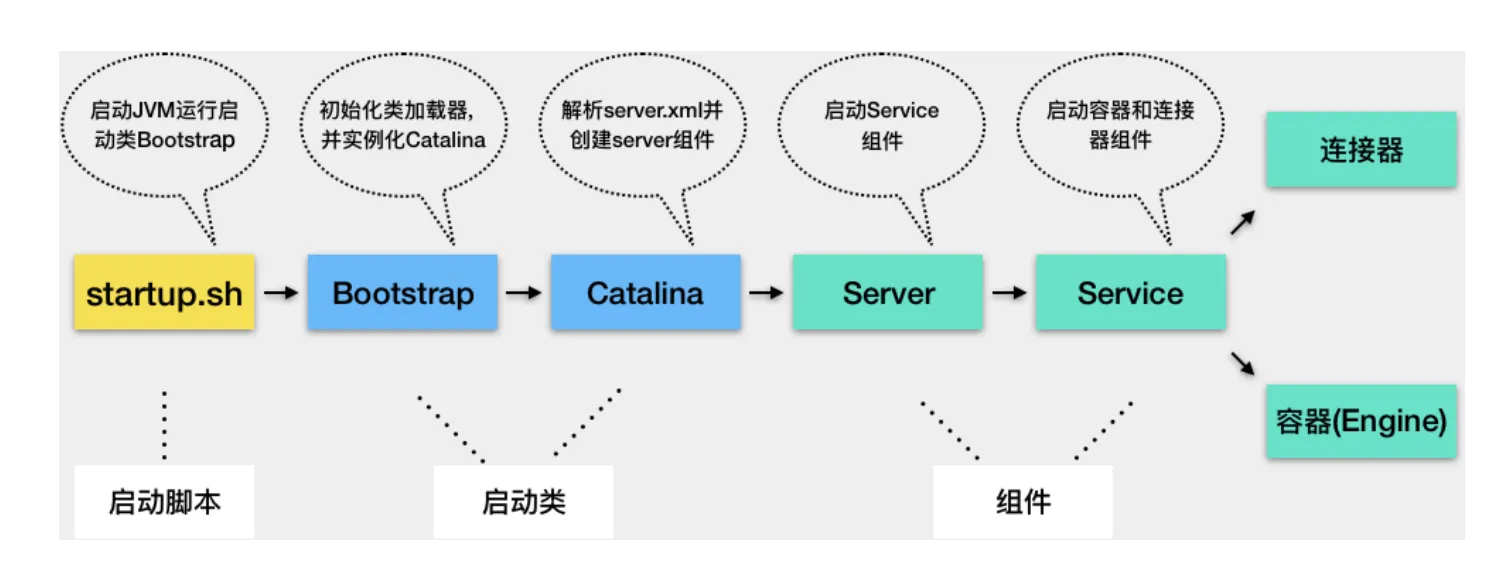 1.Tomcat 本质上是一个 Java 程序,因此 startup.sh 脚本会启动一个 JVM 来运行 Tomcat 的启动类 Bootstrap。
1.Tomcat 本质上是一个 Java 程序,因此 startup.sh 脚本会启动一个 JVM 来运行 Tomcat 的启动类 Bootstrap。
2.Bootstrap 的主要任务是初始化 Tomcat 的类加载器,并且创建 Catalina。关于 Tomcat 为什么需要自己的类加载器,我会在专栏后面详细介绍。
3.Catalina 是一个启动类,它通过解析 server.xml、创建相应的组件,并调用 Server 的 start 方法。
4.Server 组件的职责就是管理 Service 组件,它会负责调用 Service 的 start 方法。
5.Service 组件的职责就是管理连接器和顶层容器 Engine,因此它会调用连接器和 Engine 的 start 方法。
Catalina
Catalina 的主要任务就是创建 Server,它不是直接 new 一个 Server 实例就完事了,而是需要解析 server.xml,把在 server.xml 里配置的各种组件一一创建出来,接着调用 Server 组件的 init 方法和 start 方法,这样整个 Tomcat 就启动起来了。作为“管理者”,Catalina 还需要处理各种“异常”情况,比如当我们通过“Ctrl + C”关闭 Tomcat 时,Tomcat 将如何优雅的停止并且清理资源呢?因此 Catalina 在 JVM 中注册一个“关闭钩子”。
java public void start() {
if (getServer() == null) {
load();
}
if (getServer() == null) {
log.fatal("Cannot start server. Server instance is not configured.");
return;
}
long t1 = System.nanoTime();
// Start the new server
try {
getServer().start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.fatal(sm.getString("catalina.serverStartFail"), e);
try {
getServer().destroy();
} catch (LifecycleException e1) {
log.debug("destroy() failed for failed Server ", e1);
}
return;
}
long t2 = System.nanoTime();
if(log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info("Server startup in " + ((t2 - t1) / 1000000) + " ms");
}
// Register shutdown hook
if (useShutdownHook) {
if (shutdownHook == null) {
shutdownHook = new CatalinaShutdownHook();
}
Runtime.getRuntime().addShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, disable JULI's shutdown hook since
// shutdown hooks run in parallel and log messages may be lost
// if JULI's hook completes before the CatalinaShutdownHook()
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
false);
}
}
if (await) {
await();
stop();
}
}
“关闭钩子”其实就是一个线程,JVM 在停止之前会尝试执行这个线程的 run 方法。下面我们来看看 Tomcat 的“关闭钩子”CatalinaShutdownHook 做了些什么。
java protected class CatalinaShutdownHook extends Thread {
@Override
public void run() {
try {
if (getServer() != null) {
Catalina.this.stop();
}
} catch (Throwable ex) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(ex);
log.error(sm.getString("catalina.shutdownHookFail"), ex);
} finally {
// If JULI is used, shut JULI down *after* the server shuts down
// so log messages aren't lost
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).shutdown();
}
}
}
}
private static final Log log = LogFactory.getLog(Catalina.class);
}
然后调用server的stop方法,就是实现的LifeCycle接口的Stop方法
java public void stop() {
try {
// Remove the ShutdownHook first so that server.stop()
// doesn't get invoked twice
if (useShutdownHook) {
Runtime.getRuntime().removeShutdownHook(shutdownHook);
// If JULI is being used, re-enable JULI's shutdown to ensure
// log messages are not lost
LogManager logManager = LogManager.getLogManager();
if (logManager instanceof ClassLoaderLogManager) {
((ClassLoaderLogManager) logManager).setUseShutdownHook(
true);
}
}
} catch (Throwable t) {
ExceptionUtils.handleThrowable(t);
// This will fail on JDK 1.2. Ignoring, as Tomcat can run
// fine without the shutdown hook.
}
// Shut down the server
try {
Server s = getServer();
LifecycleState state = s.getState();
if (LifecycleState.STOPPING_PREP.compareTo(state) <= 0
&& LifecycleState.DESTROYED.compareTo(state) >= 0) {
// Nothing to do. stop() was already called
} else {
s.stop();
s.destroy();
}
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
log.error("Catalina.stop", e);
}
}
server组件
Server 组件的具体实现类是 StandardServer,我们来看下 StandardServer 具体实现了哪些功能。Server 继承了 LifeCycleBase,它的生命周期被统一管理,并且它的子组件是 Service,因此它还需要管理 Service 的生命周期,也就是说在启动时调用 Service 组件的启动方法,在停止时调用它们的停止方法。Server 在内部维护了若干 Service 组件,它是以数组来保存的
添加service
java @Override
public void addService(Service service) {
service.setServer(this);
synchronized (servicesLock) {
Service results[] = new Service[services.length + 1];
System.arraycopy(services, 0, results, 0, services.length);
results[services.length] = service;
services = results;
if (getState().isAvailable()) {
try {
service.start();
} catch (LifecycleException e) {
// Ignore
}
}
// Report this property change to interested listeners
support.firePropertyChange("service", null, service);
}
}
service实现类
StandardService 继承了 LifecycleBase 抽象类,此外 StandardService 中还有一些我们熟悉的组件,比如 Server、Connector、Engine 和 Mapper。
service启动
java @Override
protected void startInternal() throws LifecycleException {
if (log.isInfoEnabled()) {
log.info(sm.getString("standardService.start.name", this.name));
}
setState(LifecycleState.STARTING);
// Start our defined Container first
if (engine != null) {
synchronized (engine) {
engine.start();
}
}
synchronized (executors) {
for (Executor executor : executors) {
executor.start();
}
}
mapperListener.start();
// Start our defined Connectors second
synchronized (connectorsLock) {
for (Connector connector : connectors) {
try {
// If it has already failed, don't try and start it
if (connector.getState() != LifecycleState.FAILED) {
connector.start();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(sm.getString("standardService.connector.startFailed", connector), e);
}
}
}
}
从启动方法可以看到,Service 先启动了 Engine 组件,再启动 Mapper 监听器,最后才是启动连接器。这很好理解,因为内层组件启动好了才能对外提供服务,才能启动外层的连接器组件。而 Mapper 也依赖容器组件,容器组件启动好了才能监听它们的变化,因此 Mapper 和 MapperListener 在容器组件之后启动。组件停止的顺序跟启动顺序正好相反的,也是基于它们的依赖关系。
server接口
java */
public interface Server extends Lifecycle {
// ------------------------------------------------------------- Properties
/**
* @return the global naming resources.
*/
NamingResourcesImpl getGlobalNamingResources();
/**
* Set the global naming resources.
*
* @param globalNamingResources The new global naming resources
*/
void setGlobalNamingResources
(NamingResourcesImpl globalNamingResources);
/**
* @return the global naming resources context.
*/
javax.naming.Context getGlobalNamingContext();
/**
* @return the port number we listen to for shutdown commands.
*
* @see #getPortOffset()
* @see #getPortWithOffset()
*/
int getPort();
/**
* Set the port number we listen to for shutdown commands.
*
* @param port The new port number
*
* @see #setPortOffset(int)
*/
void setPort(int port);
/**
* Get the number that offsets the port used for shutdown commands.
* For example, if port is 8005, and portOffset is 1000,
* the server listens at 9005.
*
* @return the port offset
*/
int getPortOffset();
/**
* Set the number that offsets the server port used for shutdown commands.
* For example, if port is 8005, and you set portOffset to 1000,
* connector listens at 9005.
*
* @param portOffset sets the port offset
*/
void setPortOffset(int portOffset);
/**
* Get the actual port on which server is listening for the shutdown commands.
* If you do not set port offset, port is returned. If you set
* port offset, port offset + port is returned.
*
* @return the port with offset
*/
int getPortWithOffset();
/**
* @return the address on which we listen to for shutdown commands.
*/
String getAddress();
/**
* Set the address on which we listen to for shutdown commands.
*
* @param address The new address
*/
void setAddress(String address);
/**
* @return the shutdown command string we are waiting for.
*/
String getShutdown();
/**
* Set the shutdown command we are waiting for.
*
* @param shutdown The new shutdown command
*/
void setShutdown(String shutdown);
/**
* @return the parent class loader for this component. If not set, return
* {@link #getCatalina()} {@link Catalina#getParentClassLoader()}. If
* catalina has not been set, return the system class loader.
*/
ClassLoader getParentClassLoader();
/**
* Set the parent class loader for this server.
*
* @param parent The new parent class loader
*/
void setParentClassLoader(ClassLoader parent);
/**
* @return the outer Catalina startup/shutdown component if present.
*/
Catalina getCatalina();
/**
* Set the outer Catalina startup/shutdown component if present.
*
* @param catalina the outer Catalina component
*/
void setCatalina(Catalina catalina);
/**
* @return the configured base (instance) directory. Note that home and base
* may be the same (and are by default). If this is not set the value
* returned by {@link #getCatalinaHome()} will be used.
*/
File getCatalinaBase();
/**
* Set the configured base (instance) directory. Note that home and base
* may be the same (and are by default).
*
* @param catalinaBase the configured base directory
*/
void setCatalinaBase(File catalinaBase);
/**
* @return the configured home (binary) directory. Note that home and base
* may be the same (and are by default).
*/
File getCatalinaHome();
/**
* Set the configured home (binary) directory. Note that home and base
* may be the same (and are by default).
*
* @param catalinaHome the configured home directory
*/
void setCatalinaHome(File catalinaHome);
// --------------------------------------------------------- Public Methods
/**
* Add a new Service to the set of defined Services.
*
* @param service The Service to be added
*/
void addService(Service service);
/**
* Wait until a proper shutdown command is received, then return.
*/
void await();
/**
* Find the specified Service
*
* @param name Name of the Service to be returned
* @return the specified Service, or <code>null</code> if none exists.
*/
Service findService(String name);
/**
* @return the set of Services defined within this Server.
*/
Service[] findServices();
/**
* Remove the specified Service from the set associated from this
* Server.
*
* @param service The Service to be removed
*/
void removeService(Service service);
/**
* @return the token necessary for operations on the associated JNDI naming
* context.
*/
Object getNamingToken();
}
本文作者:yowayimono
本文链接:
版权声明:本博客所有文章除特别声明外,均采用 BY-NC-SA 许可协议。转载请注明出处!